Introduction
Self-driving car (AV) technology, often called autonomous vehicle (AV) technology, refers to the sophisticated integration of sensors, artificial intelligence, and machine learning systems that enable a vehicle to navigate and operate with reduced or no human input. It is not a single gadget but an interconnected automated driving system (ADS) that continuously perceives the environment, makes complex driving decisions, and controls the vehicle’s motion. By exploring self-driving car AV technology, you’ll gain clear insight into how artificial intelligence, sensors, and automation combine to create vehicles that think, learn, and act with precision.
Understanding self-driving car (AV) technology is critical, as it promises to redefine urban mobility, supply chains, and road safety, but its path to widespread adoption is paved with significant technical, regulatory, and ethical challenges.
What is a self-driving car?
A self-driving car is a vehicle that uses AI-driven systems, sensors, and computing power to sense its environment and navigate safely with little or no human input. Unlike traditional cars, AVs don’t just follow driver commands—they interpret data, make judgments, and take action, much like a human driver would.
Primary Entity & Core Technology
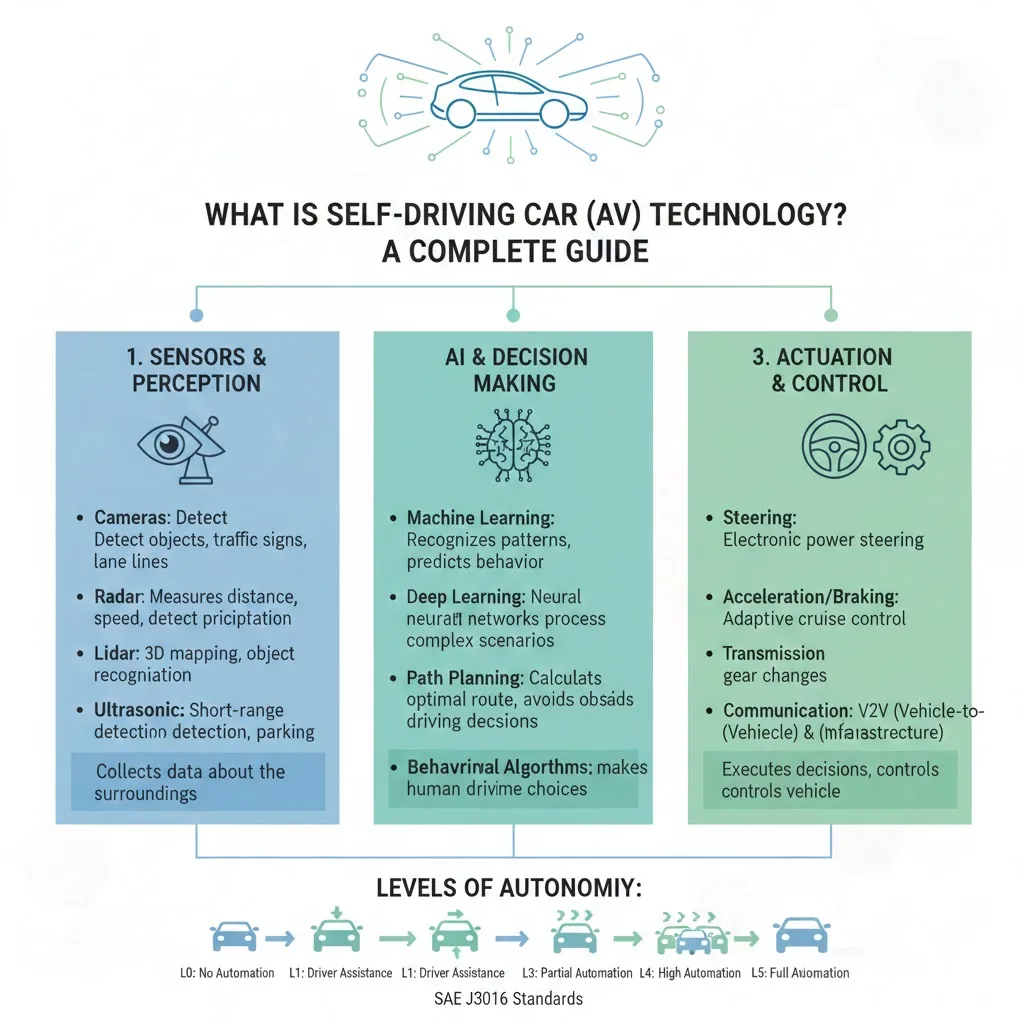
The primary entity is the automated driving system (ADS), which is distinct from common ADAS features like lane-keep assist. An ADS is responsible for the complete dynamic driving task—controlling steering, acceleration, and braking—within its defined operational design domain (ODD). The core of this system is a continuous loop of perception, decision, and action, powered by a fusion of hardware and software.
Perception: The Vehicle’s “Senses”
Modern self-driving systems primarily rely on three complementary sensor technologies to create a 360-degree, real-time model of the world:
- Cameras: Provide high-resolution, colour-rich visual data to identify lane markings, traffic signals, and road signs. They are cost-effective but can be hindered by poor lighting or adverse weather.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Uses laser pulses to create a precise, high-definition 3D map of the surroundings. It excels at measuring distances and detecting object shapes but has historically been more expensive and can struggle with heavy rain or fog.
- Radar: Utilizes radio waves to detect objects and their speed, performing reliably in all weather conditions. It is crucial for adaptive cruise control but offers lower resolution than LiDAR or cameras.
Decision: The “AI Brain”
The raw data from sensors is processed by a powerful onboard computer. Artificial Intelligence (AI), specifically deep learning and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), analyzes this information to identify objects (pedestrians, other cars), predict their behaviour, and plot a safe path. This software must interpret complex scenarios—like an obscured stop sign or a jaywalking pedestrian—and execute driving decisions that are both safe and natural within the flow of traffic.
Action: Vehicle Control
Once a decision is made, the system sends electronic commands to the vehicle’s actuators that control steering, acceleration, and braking, executing the planned maneuver.
Levels of Automation: From Assistance to Full Autonomy
Not all automation is equal. The industry standard, defined by SAE International, outlines six levels (0-5) that clarify the division of responsibility between the human driver and the machine.
- Level 0-2 (Driver Support): The human driver performs all driving tasks. Systems at these levels provide warnings (Level 0) or temporary assistance with steering or acceleration (Level 1-2), but the driver must remain constantly engaged. Most “autopilot” systems today are Level 2.
- Level 3 (Conditional Automation): The ADS can handle all driving under specific conditions (e.g., highway traffic jams). This level introduces complex liability questions.
- Level 4 (High Automation): The vehicle operates without a driver within a geofenced area or under specific conditions. If the system encounters a scenario it cannot manage, it can perform a minimal-risk maneuver, like pulling over safely.
- Level 5 (Full Automation): The vehicle can drive anywhere a human can, under all conditions, with no human intervention required. This remains a theoretical goal; no commercial system has achieved it as of 2026.
The Current State: Robotaxis and Consumer ADAS
The deployment of self-driving technology has diverged into two main paths.
- Robotaxi Services: Companies like Waymo operate commercial, driverless taxi services (Level 4) in specific, meticulously mapped urban areas like San Francisco and Phoenix. These services are expanding, with Waymo planning a London launch in 2026. They represent the most advanced public-facing AVs but operate within strict geographic and operational limits.
- Consumer Vehicles: For personal car buyers, true self-driving is not yet available. However, advanced Level 2+ systems are becoming more capable. Examples include GM’s Super Cruise, Ford’s BlueCruise, and Mercedes-Benz Drive Pilot, which offer hands-free driving on pre-mapped highways but require constant driver supervision.
Regulatory and Safety Framework
A robust regulatory framework is essential for public trust and safe deployment. The UK’s Automated Vehicles Act provides a leading example, establishing clear rules.
- The Self-Driving Test: Vehicles must be authorized and pass a statutory test proving they can drive autonomously “safely and legally,” at least as competently as a careful human driver.
- Liability and Insurance: The Act creates a crucial immunity clause for users. When an authorized self-driving feature is engaged, the human is not liable for the car’s actions; responsibility shifts to the Authorized Self-Driving Entity (e.g., the manufacturer). Insurers remain primarily liable for accidents, creating a clear claims process for victims.
- Marketing Integrity: To prevent confusion, the Act proposes strict rules against marketing cars with only driver-assist features (SAE Level 2) as “self-driving” or “autonomous.”
Potential Impacts and Challenges
The widespread adoption of self-driving cars presents a complex mix of transformative benefits and serious challenges.
Potential Benefits:
- Safety: With 94% of crashes attributed to human error, AVs could dramatically reduce accidents caused by distraction, impairment, or fatigue.
- Efficiency and Congestion: AVs can drive closer together (“platooning”), smooth traffic flow, and reduce fuel consumption and emissions by up to 10%.
- Accessibility and Productivity: They offer new mobility options for the elderly and disabled and could reclaim commute time for work or leisure.
Key Challenges:
- Technical Limitations: Handling “edge cases”—rare, unpredictable events—and performing in all weather conditions remain significant hurdles.
- Ethical and Equity Concerns: Algorithmic bias must be addressed to ensure systems detect all pedestrians equally. There are also concerns about job displacement for professional drivers and ensuring equitable access to the technology.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting vehicles from malicious hacking is a paramount safety requirement.
- Public Acceptance: Surveys show public trust is fragile; high-profile incidents can significantly dampen confidence.
The Future of AI in Self-Driving Cars
As AI models become more advanced, cars will gain human-like reasoning abilities—not just reacting to road conditions, but anticipating and adapting like skilled drivers. Future AVs will integrate with smart city infrastructure, logistics systems, and even AI-powered traffic control, creating a safer, cleaner, and more efficient transportation ecosystem.
Conclusion
Self-driving car technology represents one of the most ambitious engineering challenges of our time, blending robotics, AI, and big data to tackle the problem of human mobility. While the vision of ubiquitous, fully autonomous vehicles is compelling, the current reality is a landscape of incremental advancement, rigorous testing, and emerging regulation. The technology’s ultimate success will be measured not by its sophistication in a lab, but by its demonstrable safety, reliability, and positive integration into society. For now, the journey toward autonomy is as much about building robust legal frameworks and public trust as it is about refining algorithms. The road ahead is being mapped in real time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does AI play in self-driving cars?
AI is the “brain” of autonomous vehicles. It processes data from sensors, cameras, and radar, then makes real-time driving decisions like braking, steering, and navigating traffic.
How do self-driving cars see the road?
They use a combination of cameras, LiDAR, radar, and AI-powered computer vision to detect lane markings, pedestrians, traffic signals, and obstacles. In theory, yes—AI can reduce human errors, which cause over 90% of accidents. However, challenges remain in handling rare or unpredictable road situations.
What companies are leading in AI-powered self-driving technology?
Leaders include Waymo (Google), Tesla, Cruise (GM), Baidu, and Aurora, among others. Each uses AI differently to develop autonomous driving systems.