Introduction
In today’s digital era, many businesses and individuals ask, what is cloud computing and why is it so important? Simply put, what is cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—like storage, servers, and software—over the internet instead of relying on local hardware. By understanding what is cloud computing, users can see how it improves efficiency, reduces costs, and offers flexibility for both personal and professional needs.
Fundamentals of Cloud Computing
Defining Cloud Computing
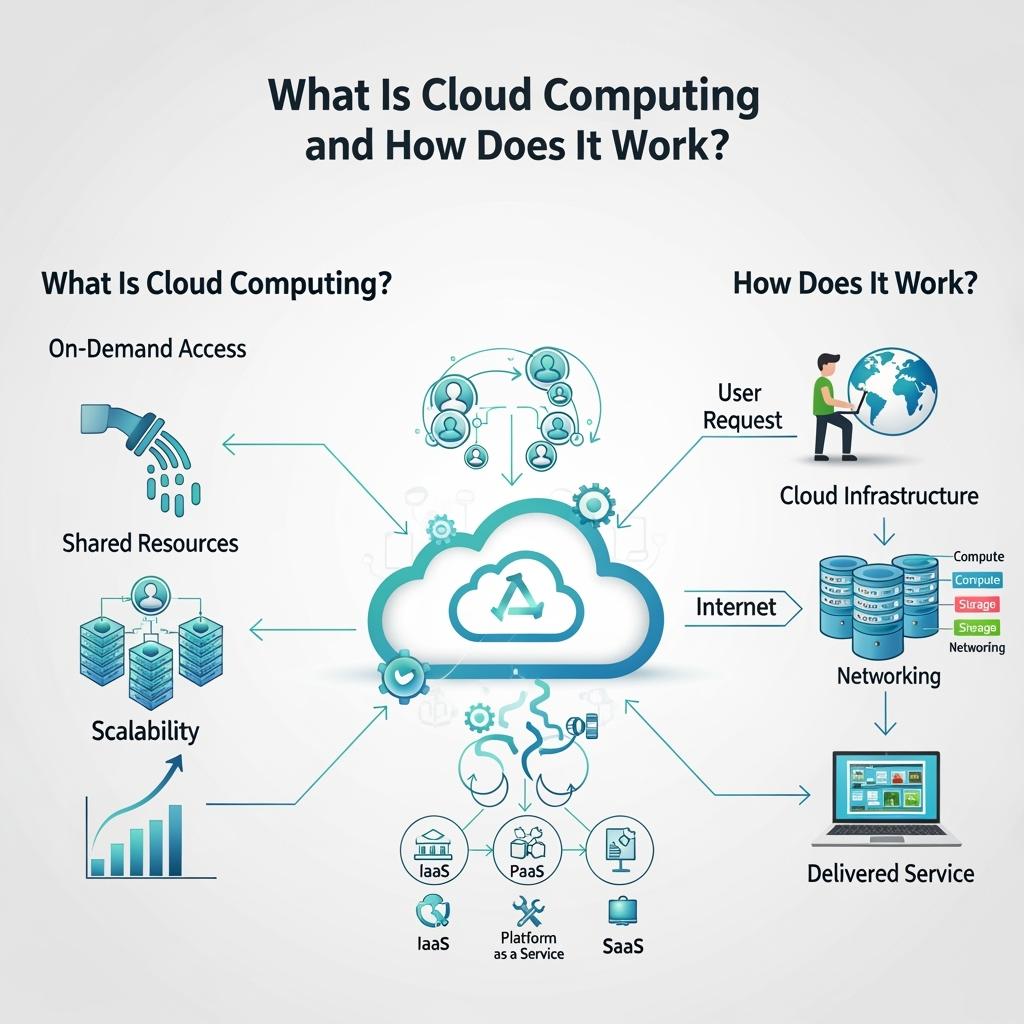
Cloud computing refers to the provision of computing services, including storage, servers, databases, networking, software, and analytics, via the internet, commonly referred to as “the cloud,” rather than depending on local hardware.
The Evolution of Computing Infrastructure
From bulky on-premises servers in the early days to today’s scalable, internet-based platforms, computing has shifted toward flexibility and efficiency. The rise of virtualization, high-speed internet, and global data centers has fueled this transformation.
Key Characteristics That Set Cloud Computing Apart
• On-Demand Access – Services are available instantly.
• Resource Pooling – Several users can safely use the same infrastructure together.
• Scalability—Resources change automatically based on what is needed.
• Assessed Service – You are charged solely for the amount you genuinely utilize.
Types of Cloud Computing Service Models
Software as a Service (SaaS): Applications at Your Fingertips
SaaS delivers ready-to-use software via the internet, eliminating the need for installation.
Example: Google Workspace provides email, document editing, and storage all in the cloud.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Development Made Simple
Platform as a Service (PaaS) equips developers with the necessary tools to design, test, and deploy applications, eliminating the requirement to manage underlying infrastructure.
Example: Heroku enables developers to launch apps without server management.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Virtual Hardware Resources
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers storage solutions and server resources that are available for your use at any time.
Function as a Service (FaaS): The Serverless Method
FaaS lets developers execute code based on events without having to set up servers.
Example: AWS Lambda runs code only when it’s activated, which helps save money.
What Is Cloud Computing, and How Does It Work? Cloud Deployment Models Explained
• Public Cloud: Accessible to anyone via a provider like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
• Private Cloud: Dedicated to one organization for better control and security.
• Hybrid Cloud: Merges public and private options for greater flexibility.
• Multi-Cloud: Uses multiple cloud providers to avoid dependency.
• Community Cloud: Shared by organizations with common goals.
Real-World Cloud Computing Examples
• Netflix—Streams content globally using AWS infrastructure.
• Spotify—Delivers personalized music experiences through Google Cloud.
• Salesforce—Pioneered SaaS for customer relationship management.
• Dropbox—Provides convenient and accessible cloud storage solutions for both individuals and organizations.
Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses
• Cost Efficiency: There’s no requirement to buy costly hardware.
• Scalability: Expand or shrink resources instantly.
• Flexibility: Work from any location with internet access.
• Automatic Updates: Always stay current with the latest features.
• Disaster Recovery: Data is backed up and protected against loss.
Cloud Computing Challenges to Consider
• Security Concerns: Sensitive data must be encrypted and access-controlled.
• Compliance Issues: Businesses must meet industry regulations.
• Bandwidth & Latency: Internet speed affects performance.
• Vendor Lock-in: Depending too much on one provider can restrict your options.
Conclusion
“What Is Cloud Computing with Examples” pertains to the provision of computing services—such as storage, databases, networking, and software—via the internet rather than through local servers. From Netflix streaming movies to Dropbox storing files, What Is Cloud Computing with Examples shows how it boosts accessibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. Understanding what cloud computing is with examples is key for businesses and individuals aiming to work smarter in the digital era.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is Cloud Computing with an Example?
It’s delivering computing services via the internet—like Netflix streaming without local storage.
Why is cloud computing important?
It reduces costs, improves scalability, and enables remote access.
What are common cloud computing examples?
Netflix, Dropbox, Spotify, Salesforce, and Google Drive.