Introduction
Conversational AI Search represents the fundamental transformation of search technology. It enables users to interact with search engines using natural, conversational language to receive direct, synthesized answers. The rise of this technology means professionals must optimize for a new environment where Conversational AI Search is the primary interface.
This requires a unified approach combining traditional technical SEO with modern stacks: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) for AI retrieval, Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) for direct answers, AI Indexing Optimization (AIO) for entity clarity, and Search Experience Optimization (SXO) for user-centric delivery. This holistic strategy is crucial for visibility in the era of Conversational AI Search.
Conversational AI Search: The Definitive Guide to the Next Era of Discovery
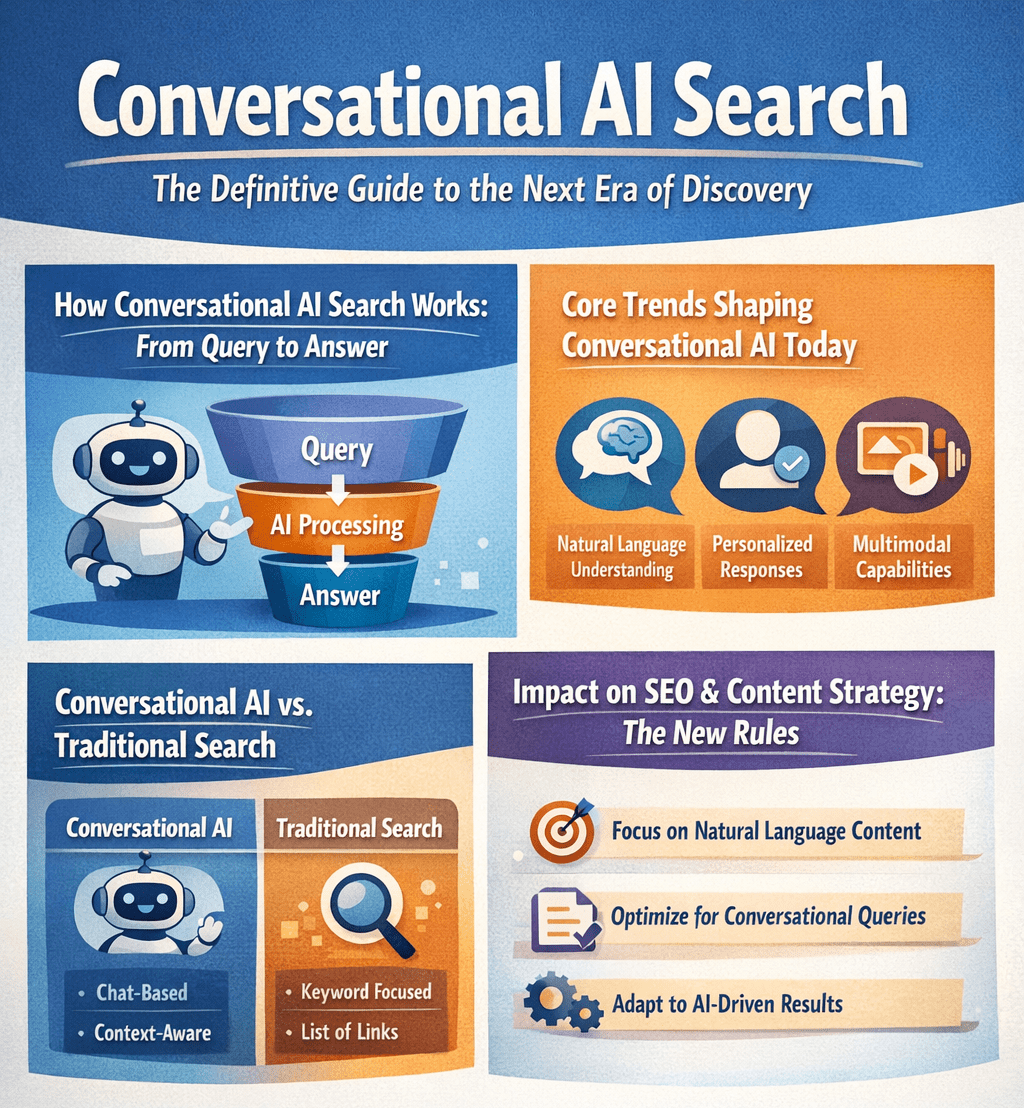
How Conversational AI Search Works: From Query to Answer
The mechanism behind conversational search is distinct from traditional systems. It starts with a user asking a full, natural language question. Advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs) parse this query to understand deep intent and context, not just keywords.
The system then performs a semantic search across its knowledge base, which includes indexed web content. Crucially, it retrieves relevant information from multiple sources and uses generative AI to synthesize a single, coherent answer. This process allows for conversational follow-ups, where the AI remembers the context of the entire dialogue, enabling a fluid, investigative conversation that mimics human interaction.
Core Trends Shaping Conversational AI Today
The evolution of this technology is being driven by several key, concurrent trends.
- The Rise of AI Agents and Zero-Click Search: AI agents are autonomous programs that can perform tasks—like researching and purchasing products—on a user’s behalf. This accelerates the “zero-click” trend, where AI Overviews provide complete answers on the results page, reducing traditional click-through rates but making pre-click visibility and citations critical new metrics for success.
- The Shift to Multimodal and Voice-First Queries: Search is becoming multimodal. Users can now search with images, voice, and text in combination. Voice search, in particular, demands a conversational keyword strategy focusing on long-tail, question-based phrases.
- The Critical Need for Structured Data and Entity Clarity: For AI to understand and recommend your content, it must be machine-readable. Implementing detailed schema markup (structured data) is non-negotiable to clearly define products, services, and brand entities. This entity optimization helps AI systems accurately place your brand within its knowledge graph.
Conversational AI vs. Traditional Search
Understanding the practical differences between these two paradigms is essential for any modern strategy. The table below summarizes the key distinctions.
| Dimension | Traditional Search | Conversational AI Search |
| Primary Output | A ranked list of links (SERP) to explore. | A single, synthesized answer or summary. |
| User Query | Short, keyword-based phrases (e.g., “best laptop 2026”). | Long, natural language questions (e.g., “What’s the best laptop for graphic design under $1500?”). |
| Interaction Model | Linear, one-and-done searches; the user manually refines keywords. | Interactive, multi-turn dialogue; AI uses context from the entire conversation. |
| User Behavior | Clicks through multiple results to compare and validate. | Evaluates the AI’s summary; may click for deeper validation on complex decisions. |
| Key Optimization Goal | Achieve a high-ranking position for target keywords. | Become a cited, trusted source within the AI-generated answer. |
Impact on SEO and Content Strategy: The New Rules
The rise of conversational AI demands a strategic pivot in search engine optimization and content creation. The foundational goal shifts from keyword rankings to topical authority and becoming a citable source.
This requires creating conversation-ready content. Structure articles with clear, question-based headers (H2/H3) and provide concise, direct answers underneath. Prioritize clarity, depth, and E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) signals, as AI systems are trained to value credible, expert sources. Furthermore, you must optimize for AI crawlers by ensuring technical SEO health, fast page speeds, and clean HTML so AI agents can access and parse your information in real time.
Practical Recommendations
To adapt, first audit your content for its value as a direct, comprehensive answer to conversational queries, not just its keyword density. Implement structured data across your site to make your content machine-friendly and to clearly define your key entities.
Develop a content strategy that embraces the hybrid search landscape. Continue targeting high-intent transactional queries via traditional SEO, while creating in-depth, expert-led informational content designed to be cited by AI for top-of-funnel discovery. Finally, track new metrics like AI impression share, citation frequency, and the quality of AI-referred traffic, not just organic clicks and positions.
FAQs
Does conversational AI search mean traditional SEO is dead?
No. Traditional SEO fundamentals—technical health, quality content, and a good user experience—are now the essential foundation for AI visibility. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) builds upon this foundation to optimize for AI citation.
What kind of traffic can I expect from AI search?
Volume from AI referrals is currently lower than traditional organic traffic, but it is growing exponentially and is often higher in intent and quality. Users who click have already received a summarized answer and are seeking deeper validation or are ready to act.
How do I optimize for voice search and AI assistants?
Focus on long-tail, question-based keywords that mirror natural speech. Structure content to provide clear, direct answers, and ensure your local business information (via schema markup) is accurate for “near me” queries.