Introduction
The emergence of the AI Robot Hospital in China marks a pivotal shift from concept to reality in global healthcare. This model, exemplified by Tsinghua University’s “Agent Hospital,” represents a hybrid system where human expertise directs a team of autonomous AI agents. The core promise of this AI Robot Hospital in China is to address systemic issues like physician shortages and operational inefficiency. By integrating human oversight with robotic precision, this new paradigm for an AI Robot Hospital in China aims to redefine patient care delivery.
What Is an AI Robotic Hospital?
An AI robotic hospital is a fully integrated care environment where intelligent agents perform clinical tasks. It is not a physical building of metal robots but a sophisticated digital ecosystem. At its heart is a self-evolving AI framework that powers virtual doctor and nurse agents capable of diagnosing conditions, creating treatment plans, and managing patient follow-up autonomously. These systems are trained on vast libraries of synthetic patient cases, allowing them to simulate and handle thousands of patient interactions in days—a task that would take human teams years.
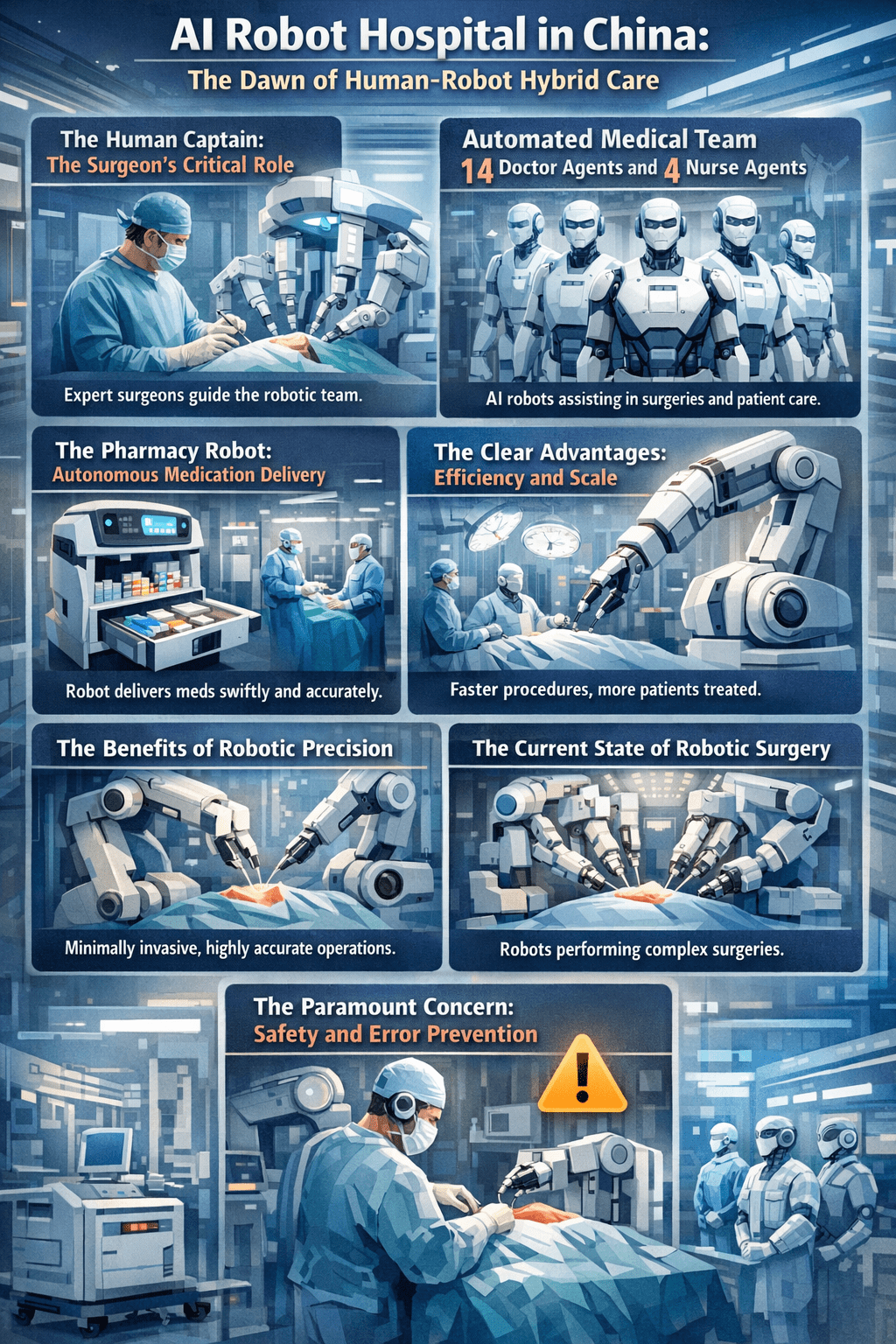
The Human Captain: The Surgeon’s Critical Role
In this advanced setup, the human surgeon, such as the hypothetical Dr. Alfred, is not replaced but elevated. His role transitions from performing every procedure to being a system overseer and final authority. He monitors the AI agents’ decisions, intervenes in complex or edge-case scenarios, and provides the irreplaceable human judgment for ethical and nuanced care. This model leverages human cognitive skills for supervision, strategy, and empathy, while delegating repetitive, data-intensive tasks to the AI team.
Automated Medical Team: 14 Doctor Agents and 4 Nurse Agents
The robotic workforce is comprised of specialized AI agents. Typically, a configuration includes 14 doctor agents across various specialties and four nurse agents for support tasks. These are not physical robots but software entities that interact within a simulated hospital environment. They can consult with each other, access medical databases in real-time, and simulate the entire patient journey from admission to discharge. Their performance is notable, with reported diagnostic accuracy rates of over 93% on standardized medical exam questions.
The Pharmacy Robot: Autonomous Medication Delivery
Beyond diagnosis, automation extends to logistics. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), like the “Medbot,” are deployed for secure, 24/7 medication delivery. These robots navigate hospital corridors and elevators, transporting pharmaceuticals directly from the pharmacy to patient wards or nursing stations. This system ensures timely administration, reduces manual errors in hand-offs, and frees pharmacy and nursing staff for more critical, patient-facing duties.
The Clear Advantages: Efficiency and Scale
The benefits of this model are transformative. The most immediate advantage is the drastic reduction in patient wait times for initial consultation and routine follow-ups. Furthermore, it offers immense scalability, capable of managing thousands of patients daily, which is crucial for large populations or during health crises. It also serves as a risk-free training ground for medical students, who can practice on virtual patients without real-world consequences.
The Benefits of Robotic Precision
The main advantages of this approach are
- Minimally Invasive: Procedures are done through tiny incisions, avoiding large openings (like splitting the chest bone in traditional heart surgery).
- Faster Patient Recovery: Smaller incisions typically mean less pain, shorter hospital stays, and a quicker return to normal activities compared to open surgery.
The Current State of Robotic Surgery
Today’s surgical robots, like the widely used da Vinci system, are advanced tools controlled entirely by human surgeons. They are not autonomous “doctors.”
- Human Control: The surgeon operates from a console, with the system translating their hand movements into precise motions of miniaturized instruments inside the patient.
- Future Potential: Research is exploring machine learning to eventually enable robots to perform certain parts of procedures autonomously or act as a “fail-safe,” but this remains under development and requires extensive safety measures.
The Paramount Concern: Safety and Error Prevention
However, the critical question remains: is it safe? The risks of wrong medication or incorrect treatment are the primary concerns. While AI agents achieve high accuracy in controlled tests, real-world medicine is fraught with ambiguities. A misdiagnosis or a drug interaction error could have serious consequences. The safety architecture, therefore, hinges on multiple layers: rigorous validation of the AI’s recommendations, seamless human-over-the-loop monitoring, and robust physical checks in systems like automated drug dispensers.
The Future and the Ethical Frontier
The logical progression points toward autonomous robotic surgeons. While current systems assist human surgeons, the development of AI capable of independent surgical intervention represents the frontier of both technical research and profound ethical deliberation. This raises critical questions about liability, regulation, and the very nature of trust in medicine. The future will be defined by finding the optimal balance between robotic efficiency and indispensable human judgment.
Conclusion
The AI robot hospital is not a distant sci-fi scenario but an unfolding reality in China. Its potential to expand access and streamline care is monumental. Yet, its successful integration into global healthcare will depend entirely on our ability to engineer not just smarter machines, but also smarter safety protocols, ethical guidelines, and collaborative care models. The goal is not a hospital without humans, but a better hospital that empowers both its human and robotic caregivers.
Recommendation
For healthcare administrators observing this trend, the next step is strategic evaluation. Begin by auditing internal processes that are high-volume and rule-based, as these are prime for initial automation. Prioritize partnerships with technology providers that emphasize transparent AI and built-in human oversight protocols. Investing in staff training for hybrid human-AI collaboration will be as crucial as investing in the technology itself.
FAQs
Are robot doctors replacing human doctors?
No. They are designed to augment human teams, handling routine tasks to allow doctors to focus on complex diagnosis, surgery, and patient communication.
How accurate are AI doctor diagnoses?
In testing environments like the MedQA dataset, they have shown accuracy over 93%. However, real-world clinical accuracy requires continuous validation and human oversight.
Who is responsible if a robot makes a medical error?
Liability is a complex, evolving area. Typically, responsibility lies with the hospital deploying the system and the human professionals overseeing it, underscoring the need for clear governance frameworks.