What is Big Data Technology: A Complete Guide
Introduction
In the modern digital era, data has become a driving force behind innovation and strategic growth. Big Data Technology addresses the methods and tools used to manage, process, and analyze vast volumes of information effectively. By understanding Big Data Technology, organizations can leverage data-driven insights to enhance decision-making, optimize operations, and stay competitive.
Exploring Big Data Technology provides clarity on how businesses transform raw data into actionable value in today’s fast-paced technological landscape.
What is Big Data Technology?
Big data technology includes a range of tools, fabrics, and styles designed for storing, recycling, and assaying large and complex datasets that traditional databases and software find difficult to manage. These technologies help associations uncover precious perceptivity from vast quantities of structured, semi-structured, and unshaped data collected from colorful sources such as social media, IoT bias, sale logs, and detectors.
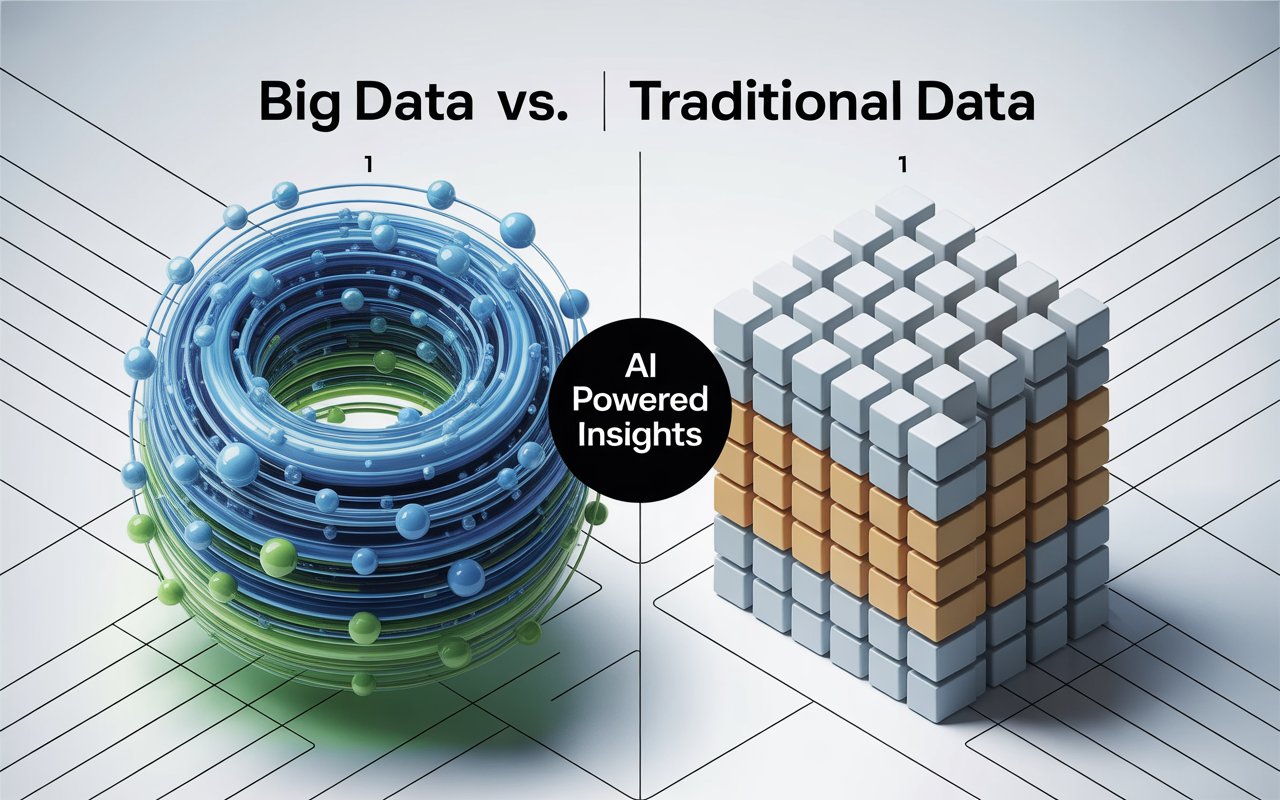
Big Data vs. Traditional Data?
The primary difference between Big Data vs. Traditional Data lies in volume, variety, velocity, and complexity. Traditional data is structured, smaller in scale, and manageable with relational databases, whereas Big Data involves massive, unstructured, or semi-structured datasets processed in real time using advanced technologies. Understanding the difference between Big Data vs. Traditional Data helps organizations choose the right data management strategy for scalability, efficiency, and informed decision-making.
Big Data vs. Traditional Data: Key Differences
| Feature | Traditional Data | Big Data |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | Limited and smaller datasets, easy to manage | Massive datasets in petabytes or more |
| Variety | Mostly structured (tables, spreadsheets) | Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured (text, video, IoT) |
| Velocity | Processed in batches at slower speeds | Real-time or near real-time data processing |
| Complexity | Less complex, handled by relational databases (RDBMS) | Highly complex, requires distributed frameworks (Hadoop, Spark) |
| Cost | Lower storage and processing costs | Higher costs, but scalable with cloud-based solutions |
| Use Cases | Transaction records, CRM, financial reports | Predictive analytics, IoT, AI, business intelligence |
Popular Big Data Processing Frameworks
• Apache Hadoop—A foundational open-source framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets, built around the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and MapReduce programming model.
• Apache Spark—Known for in-memory computing, Spark offers lightning-fast batch and stream processing capabilities.
• Apache Flink—Specializes in real-time stream processing with high fault tolerance.
• Apache Storm—Designed for real-time data processing and managing low-latency computations.
Data Storage Solutions for Big Data
• Distributed File Systems—HDFS remains the most popular, but alternatives like Ceph and Amazon S3 provide scalable storage.
• NoSQL Databases—MongoDB, Cassandra, and HBase offer flexible schema designs and high scalability.
• Data Warehouses—Amazon Redshift and Google BigQuery provide high-performance analytical processing.
• Data Lakes – Enable storage of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data for advanced analytics.
Big Data Analytics Tools
• SQL-on-Hadoop—Tools such as Hive, Impala, and Presto enable the querying of large datasets with the use of well-known SQL syntax.
• Machine Learning Libraries—TensorFlow, Scikit-learn, and MLlib power predictive analytics and AI applications.
• Business Intelligence (BI) Platforms—Tableau and Power BI transform raw data into interactive dashboards.
• Streaming Analytics—Kafka Streams and Spark Streaming enable real-time data insights.
Cloud-based Big Data Services
• Amazon Web Services (AWS)—Offers services like EMR, Redshift, and Kinesis for big data workloads.
• Google Cloud Platform (GCP)—Provides BigQuery, Dataflow, and AI tools for analytics.
• Microsoft Azure—Features Azure Synapse Analytics and HDInsight for scalable big data processing.
• IBM Cloud—Known for enterprise-level analytics and AI-driven data solutions.
Emerging Trends in Big Data Technology
• Edge Computing—Processes data closer to the source for faster decision-making.
• AI and Deep Learning—Enhance data analysis with advanced pattern recognition and automation.
• Blockchain Integration – Improves data security, integrity, and translucency.
• Quantum Computing—Holds the potential to revolutionize big data processing speed and complexity handling.
Conclusion
In conclusion, big data plays a crucial role in transforming raw information into meaningful predictive insights that drive smarter decisions, digital transformation, and innovation, while traditional data works for routine business operations. By adopting the right technologies and strategies, associations can unleash new openings, ameliorate effectiveness, and gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are big data technologies?
Big data technologies are tools, frameworks, and platforms used to store, process, and analyze large and complex datasets that traditional systems cannot handle efficiently.
Which are the most widely used big data technologies?
Popular ones include Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Flink, MongoDB, Cassandra, Amazon Redshift, and Google BigQuery.
What is the main difference between big data and traditional data?
Traditional Data is smaller, structured, and easier to process, while Big Data is massive, diverse, and requires advanced tools for real-time analysis.