Introduction
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is the frontier of artificial intelligence research, representing a hypothetical machine with intelligence that matches or exceeds human cognitive abilities across virtually all domains. Often referred to as Strong AI or human-level AI, an Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) system would possess the ability to understand, learn, reason, and autonomously apply its intelligence to solve any novel problem.
This contrasts sharply with today’s prevalent Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), which is confined to specific, predefined tasks. The pursuit of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is a central, stated goal for leading technology organizations, yet its achievement remains a profound theoretical challenge with immense implications for society.
Defining the Core Concept: AGI Explained
AGI is defined by its generality. While narrow AI excels within a predefined scope—like filtering spam or recommending a product—AGI implies a flexible intellect capable of transferring knowledge. An AGI system could theoretically diagnose a disease, compose a symphony, and develop a business strategy, applying core reasoning to unfamiliar challenges without task-specific programming. This capability for autonomous learning and adaptability is what distinguishes the theoretical concept of AGI from all existing AI. Researchers often use related terms like Strong AI or General AI to describe this level of machine capability.
AGI vs. Narrow AI: The Defining Divide
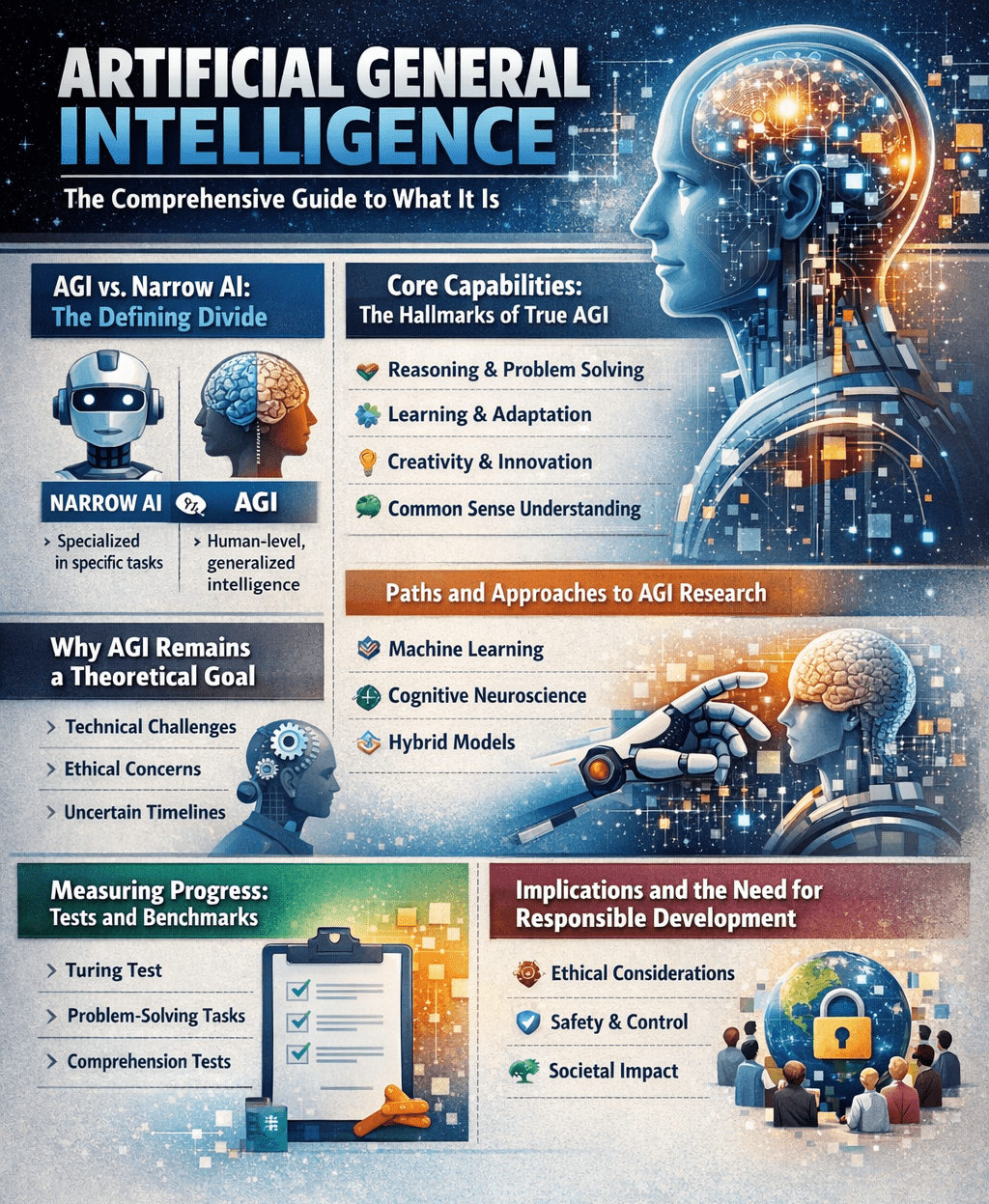
The most critical distinction in AI is between AGI and Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), also known as Weak AI. ANI constitutes all AI in existence today. These are highly specialized systems that excel within a strictly bounded domain, such as voice assistants like Siri, recommendation algorithms on Netflix, or image recognition software.
These systems operate based on predefined rules, extensive training on specific datasets, and pattern recognition. However, they lack generalization; a chess-playing AI cannot apply its strategic reasoning to manage a supply chain or compose music. In contrast, AGI implies a flexible, autonomous intellect capable of transfer learning—taking knowledge from one domain and applying it creatively to another without task-specific reprogramming.
Core Capabilities: The Hallmarks of True AGI
For a system to be considered AGI, researchers generally agree it must demonstrate a suite of integrated, human-like cognitive abilities. These include:
- Reasoning and Problem-Solving: Using logic, strategy, and judgment under uncertainty to tackle novel challenges.
- Knowledge Representation and Common Sense: Holding a broad, implicit understanding of how the physical and social world works.
- Planning and Learning: Autonomously setting goals, acquiring new skills, and adapting to new information.
- Natural Language Communication: Understanding and generating language with true comprehension of meaning and context.
Crucially, an AGI must be able to integrate all these skills to accomplish any given goal, moving beyond isolated competencies to unified intelligence.
Why AGI Remains a Theoretical Goal
Despite rapid progress in AI, true AGI does not exist. Modern Large Language Models (LLMs) and generative AI tools showcase impressive pattern recognition and content generation but operate as sophisticated statistical models without genuine understanding or reasoning. The leap from ANI to AGI involves monumental scientific hurdles that current paradigms have not solved.
Key challenges include instilling robust common sense reasoning and causal reasoning—the ability to understand why things happen, not just correlate that they do. Other significant obstacles involve replicating human-like creativity, achieving reliable transfer learning between unrelated domains, and integrating sensory perception and robotics for embodied interaction with the physical world.
Paths and Approaches to AGI Research
The field explores several theoretical pathways to achieving AGI:
- The Symbolic Approach: Aims to represent knowledge and human thought through expansive logic and rule-based networks.
- The Connectionist (Emergentist) Approach: Focuses on replicating the brain’s structure using neural networks, the foundation of modern deep learning and LLMs.
- The Hybrid Approach: Seeks to combine symbolic logic with connectionist sub-symbolic processing for more robust reasoning.
- Whole Organism Architecture: Believes AGI requires a physical body to learn from interaction with the environment, integrating robotics and AI.
No single approach has proven sufficient, indicating that a future breakthrough may require a synthesis of these ideas or a completely novel paradigm.
Measuring Progress: Tests and Benchmarks
How do we track advancement toward such an ambitious goal? The classic Turing Test—where a machine must convince a human it is human through conversation—is now considered an insufficient measure of deep intelligence. Researchers have proposed more rigorous, capability-based tests, such as the Coffee Test (making coffee in an unfamiliar kitchen), the Ikea Test (assembling furniture from instructions), or the Employment Test (performing an economically valuable job at a human level).
Leading labs have also developed classification frameworks. For example, researchers at Google DeepMind have proposed five levels of AGI performance, from “Emerging” (comparable to unskilled humans) to “Superhuman,” providing a more nuanced scale for evaluation.
Implications and the Need for Responsible Development
The potential development of AGI carries societal and geopolitical implications that are profound and complex. It promises revolutionary benefits in science, medicine, and industry but introduces significant risks, including economic disruption, ethical dilemmas, and questions of control and safety (AI alignment).
A key determinant of the future geopolitical landscape will be the degree of centralization in AGI development—whether it is controlled by a single entity, a few nation-states, or developed in a more decentralized manner. This makes the responsible pursuit of AGI, governed by robust ethical frameworks and international cooperation, one of the most consequential challenges of our time.
Conclusion
Artificial General Intelligence remains the defining horizon of AI—a goal that challenges our understanding of intelligence itself. Moving forward, informed discourse must balance ambitious inquiry with technical realism and ethical foresight. By grounding the discussion in clear definitions and present realities, we can engage with AGI’s development thoughtfully. To navigate this evolving landscape, commit to continuous learning focused on the substantive technical, ethical, and policy milestones that will ultimately shape this transformative technology.
Recommendations
For professionals and organizations, the most pragmatic approach is to build expertise in current narrow AI and machine learning applications, which are delivering tangible value today. Evaluate AI projects based on concrete problem-solving, not AGI hype. Develop strategic foresight by monitoring advancements in AI safety and governance. The essential next step is to cultivate a sophisticated, realistic understanding of present-day AI’s capabilities and limits, forming a solid foundation for critically assessing the future trajectory of the field.
FAQs
Is AGI the same as sentient or conscious AI?
No. AGI is defined by broad cognitive capability and problem-solving prowess. Sentience (subjective experience) and consciousness are separate philosophical concepts not required for an AI to be considered generally intelligent.
How do today’s large language models (like ChatGPT) relate to AGI?
Large language models are advanced forms of narrow AI. They generate human-like text by recognizing statistical patterns but lack true understanding, reasoning, and autonomy. They represent a step in capability but are not AGI themselves.
When will AGI be achieved?
There is no consensus, and predictions vary widely. Leading experts emphasize that fundamental breakthroughs in reasoning, understanding, and safety are required first, and a credible timeline remains elusive.