Introduction
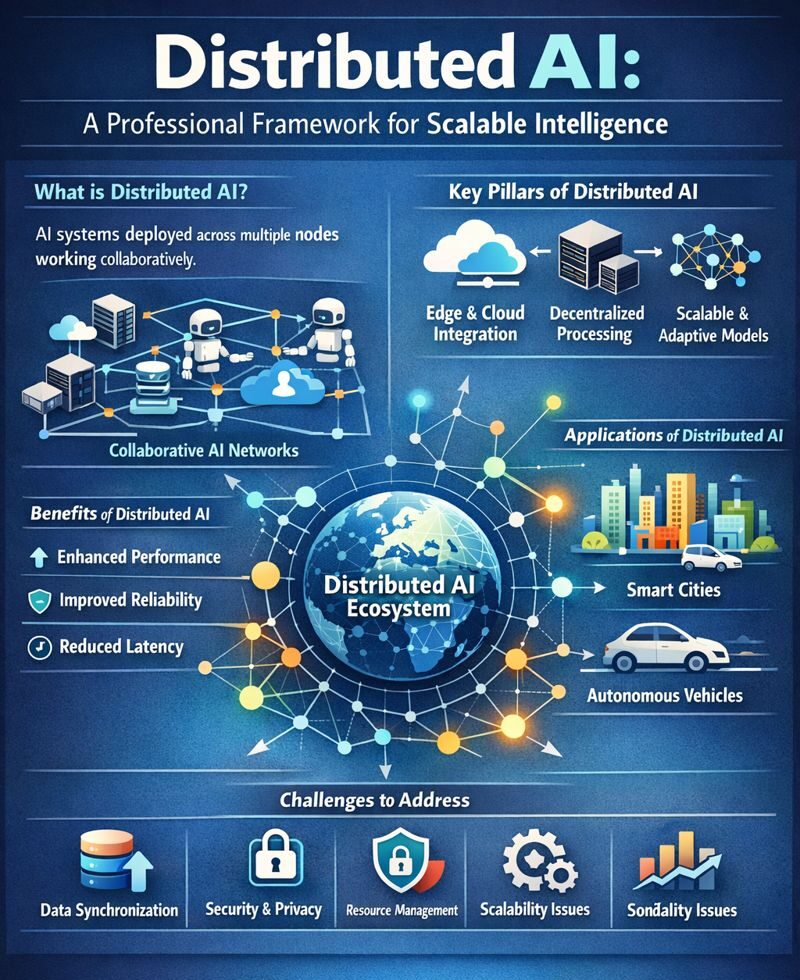
Distributed AI refers to artificial intelligence systems where data processing, reasoning, and learning occur across multiple nodes, devices, or agents rather than a single central model. This decentralized AI architecture improves scalability, reduces latency, enhances data privacy, and increases fault tolerance, especially in environments requiring real-time decision-making and regulatory compliance.
Distributed AI enables distributed machine learning by allowing models to train and operate across edge devices, cloud infrastructure, and autonomous agents without central data aggregation. In practical deployments, Distributed AI integrates edge AI for low-latency inference, federated learning for privacy-preserving collaboration, multi-agent systems for coordinated decision-making, and cloud-edge architectures for orchestration and governance, forming a resilient foundation for collaborative intelligence at scale.
How Distributed AI Differs from Centralized AI
Distributed AI decentralizes inference and learning, unlike traditional AI that centralizes data and computation. Centralized AI can become inefficient when data volumes grow or legal constraints restrict data movement. Distributed AI enables AI capabilities at the network edge, improving responsiveness and reducing data transfer overhead.
In enterprise logistics, distributed AI can localize routing decisions while feeding aggregate insights back to central optimization engines.
Federated Learning: Privacy-Centric Model Collaboration
Federated learning is a core distributed AI mechanism where multiple devices collaboratively train a shared model while keeping raw data local. Only model updates are communicated for aggregation, protecting data privacy and limiting data movement.
In healthcare, federated learning enables hospitals to improve diagnostics without sharing sensitive patient records. This aligns with data sovereignty requirements in regulated markets.
Edge AI: Real-Time Decisions at the Source
Edge AI deploys intelligent models directly on devices (sensors, gateways, and vehicles) to process data locally. This improves latency, reduces bandwidth usage, and enables autonomous action.
For example, autonomous vehicles rely on edge models for immediate decisions while streaming only summaries or critical insights to central platforms.
Multi-Agent Systems and Collaborative Intelligence
Multi-agent systems involve autonomous agents working collaboratively to solve problems that single systems cannot. These agents communicate, negotiate, or coordinate to achieve collective goals. This capability enables robust distributed AI applications where independent nodes contribute to overall intelligence.
In financial advisory systems, one agent might gather market data, another models risk, and a third executes insights—all coordinated to support enterprise decisions.
Swarm Intelligence and Decentralized Coordination
Swarm intelligence is inspired by decentralized natural systems like ant colonies. Simple, locally interacting agents produce complex global behavior. In operational systems, this approach aids distributed decision-making without a central controller, reinforcing resilience and scalability.
Cloud-Edge Coordination and Model Parallelism
Distributed AI often uses cloud infrastructure for model coordination while offloading real-time tasks to edge nodes. Model parallelism and frameworks like Horovod enable training large models across multiple machines or GPUs efficiently, distributing workload to optimize performance.
This hybrid architecture supports both global learning and local inference where appropriate.
Regulatory Alignment and Data Sovereignty
Distributed AI supports data sovereignty by keeping data in jurisdictional boundaries and transmitting insights instead of raw data. This is critical for sectors such as finance and public health, where personal data regulation is strict.
Trade-Offs and When Not to Use Distributed AI
Complex orchestration, security management, monitoring, and debugging are harder across many nodes. For simple workflows or small datasets, centralized AI can outperform distributed systems in efficiency.
The crucial evaluation is operational fit: Does intelligence need to be local, or can it be central?
Conclusion
Distributed AI reshapes how intelligent systems operate by balancing locality, privacy, and coordination. Integrating federated learning, edge AI, and multi-agent systems into enterprise architectures enables AI at scale while respecting real-world constraints. Organizations that adopt these models thoughtfully can achieve responsive, secure, and compliant intelligence. Evaluate architectures carefully and align them with business outcomes to realize distributed AI’s potential.
FAQs
What is Distributed AI?
A system where AI tasks like learning and inference are spread across multiple nodes rather than centralized.
How does federated learning enhance privacy?
It keeps raw data local and only shares aggregate model updates.
Is distributed AI always better than centralized AI?
Not always—it depends on latency, privacy needs, and system complexity.