Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) in Smart Cities now underpins the infrastructure and everyday experiences of urban living. In cities across the UK, USA, and worldwide, AI systems optimize critical services—from utilities and transportation to safety, healthcare, and personal devices. These systems leverage machine learning, connected sensors, real‑time analytics, and predictive models to adapt dynamically, reduce waste, save energy, and enhance comfort and sustainability. The breadth of AI integration ranges from autonomous vehicles and smart grids to AI‑enabled consumer technology, reshaping how cities function and how individuals live within them.
Smart Cities represent the most significant transformation in urban infrastructure since electrification. Cities across the UK and USA deploy artificial intelligence throughout their core systems to manage resources, predict failures, and respond to citizen needs in real time. This integration touches every aspect of urban life, from water distribution to emergency response.
The scope of Smart Cities extends beyond simple automation. Machine learning algorithms analyze millions of data points from sensors embedded throughout urban environments. These systems coordinate traffic signals with weather patterns, synchronize energy grids with consumption forecasts, and match housing availability with resident needs. The result is infrastructure that adapts rather than operates on fixed schedules.
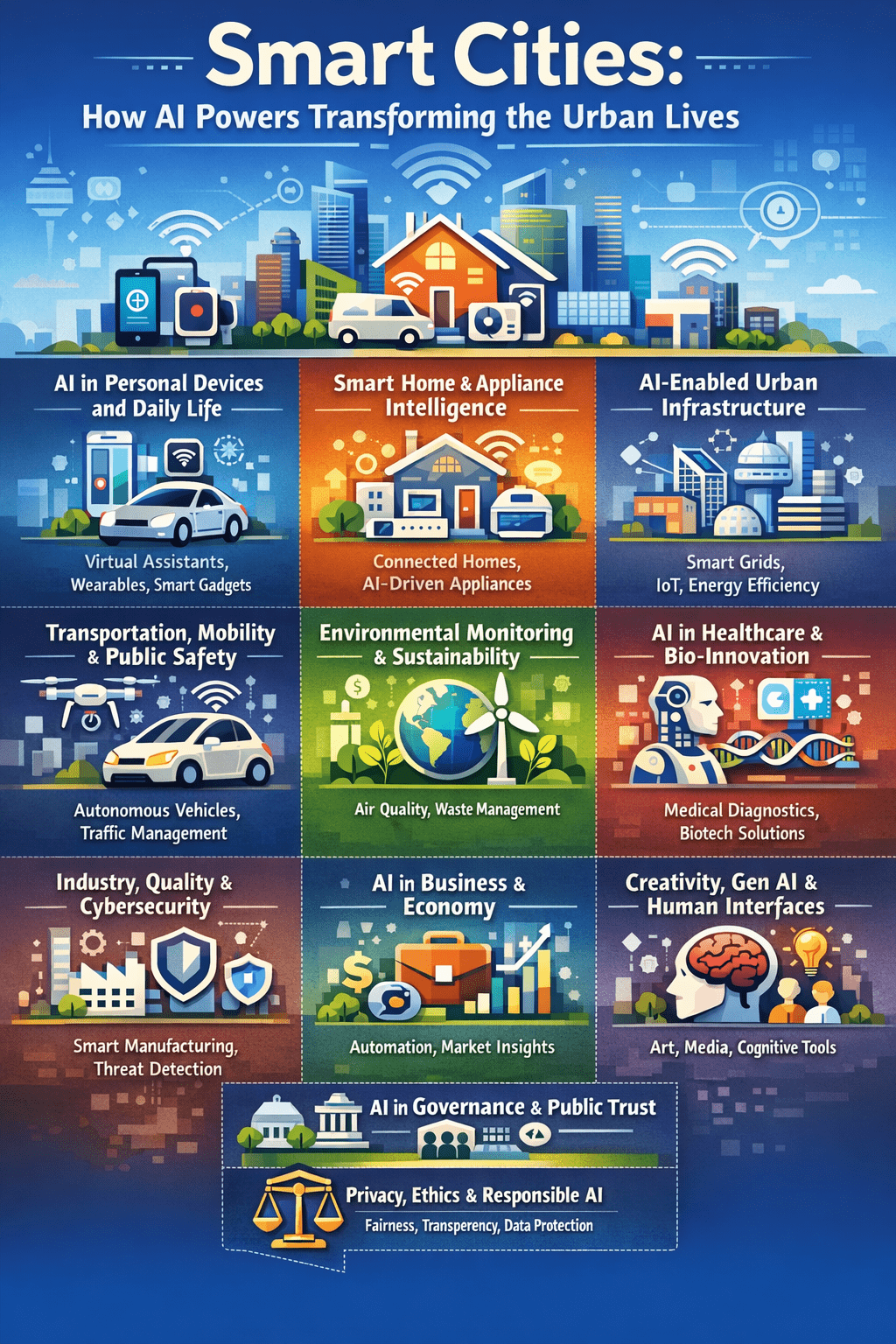
AI in Personal Devices and Daily Life
AI in Smartphones
AI manages performance and power in smartphones, optimizing task scheduling, battery longevity, and adaptive interfaces. Intelligent cameras use machine learning for low‑light performance and object recognition, while assistants like Siri and Google Assistant provide natural language interaction, predictive scheduling, and personalized insights.
AI in Computers and Laptops
AI enhances security through real‑time malware detection, automates routine tasks, supports content creation, and suggests ergonomic adjustments to reduce strain during long sessions.
AI in Toothbrushes and Pillows
Smart toothbrushes use AI to analyze brushing patterns, guiding users toward better dental health, while AI‑enabled pillows monitor sleep cycles and adjust comfort dynamically, integrating with room climate systems for holistic wellness.
Smart Home and Appliance Intelligence
Connected AI appliances extend city intelligence into daily life:
- Smart refrigerators with inventory tracking and meal suggestions.
- AI air conditioners that adapt climate based on occupancy and environmental data.
- AI washing machines that tailor cycles to fabric and load.
These devices optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and align with broader energy grid responsiveness to balance supply and demand.
AI‑Enabled Urban Infrastructure
AI in Energy Grids and Power Systems
AI predicts energy demand, matches generation with fluctuating consumption, and integrates renewables such as solar and wind into city grids. Smart meters and predictive modeling reduce outages and improve resilience. Research shows that AI‑powered energy optimization significantly enhances operational stability and efficiency in distributed energy systems.
Biological Energy and Waste Conversion
AI helps waste‑to‑energy systems maximize electricity output from organic waste, using microbial fuel cells and anaerobic digestion. Robotic sorting and predictive routing improve sustainability and minimize landfill impact.
Smart Water Management
AI detects leaks, forecasts infrastructure stress, and optimizes treatment processes in real time, improving safety and lowering chemical usage. Predictive systems enable rapid responses and reduce waste.
Housing, Urban Planning & Building Efficiency
AI systems regulate smart building operations (lighting, climate, and maintenance), match social housing with need efficiently, and expedite permit processing using document‑AI and compliance checks.
Transportation, Mobility, and Public Safety
Smart Traffic and Public Transit
AI traffic management dynamically adjusts signals, minimizes delays, and predicts congestion. Adaptive mobility systems exemplify improved urban flow and reduced emissions through data‑driven routing, consistent with high‑impact findings on AI mobility optimization in literature.
Autonomous Mobility
Innovations such as Waymo robo‑taxis, Volocopter air taxis, and SkyPod pods integrate AI for safe, efficient urban transport. Smart parking systems and EV charging networks balance grid load via predictive analytics.
Surveillance and Safety Networks
AI‑enabled smart cameras offer behavior analysis and crowd insights, feeding real‑time data into emergency systems. Combined with gunshot detection and predictive policing, these solutions enhance citywide safety.
Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability
AI continuously measures air quality, water health, and noise pollution, using distributed sensors and wearables to create hyperlocal environmental maps. Flood forecasting models merge rainfall, soil, and drainage data for early warnings, improving urban resilience.
AI in Healthcare, Life Sciences, and Bio‑innovation
Diagnostics and Medical Systems
AI interprets medical imaging and genomic data, improving early detection and care routing. Telemedicine platforms expedite consultations and monitor chronic conditions remotely.
Artificial Organs and Heart Technologies
AI‑controlled artificial hearts and hybrid organs autonomously adapt to physiological signals, while AI‑assisted clinical monitoring improves outcomes in heart‑related care.
Artificial Womb Technology
Emerging AI studies track embryo development within artificial womb systems, offering insights into neonatal health and reproductive science.
AI in Drug Discovery & Supply Chains
Platforms like Atomwise and Insilico Medicine employ AI to predict molecular interactions, optimize drug candidates, and streamline clinical pipelines. AI also forecasts drug demand and supply shortages, improving public health readiness.
Quality, Industry, and Cybersecurity
Quality Index and Industrial AI
Machine vision inspects manufacturing lines and urban infrastructure, ensuring compliance with standards and minimizing risk. AI monitors power plant outputs, detects anomalies, and supports automated remediation.
Cybersecurity
AI identifies threats, predicts attacks, and protects smart city infrastructure, from energy grids to healthcare and transport networks. Real‑time threat intelligence adapts dynamically to evolving risks, strengthening critical systems.
AI in Business, Workforce, and Economy
Business Intelligence
AI forecasts sales, optimizes staffing, personalizes customer experiences, analyzes risk, and segments marketing audiences. These capabilities elevate decision-making and operational agility.
Workforce Transformation
Automation of repetitive tasks, AI‑powered reskilling platforms, and augmented cognitive tools reshuffle job roles. Emerging AI careers—such as AI strategists, data curators, and AI operations managers—reflect the shift toward knowledge‑driven work.
Creativity, Gen AI, and Human Cognition Interfaces
Content, Graphics, and App Creation
AI tools streamline graphics, video, and image editing, generate UI/UX code, and automate app development via platforms like Adobe Sensei and GitHub Copilot.
Avatars, Voice Cloning, and Dream Interfaces
AI creates realistic avatars, synthesizes voices, and explores neural pattern interpretation. BCIs and cognitive interfaces combine AI with EEG analysis for emerging applications such as dream decoding and cognitive health research.
AI in Governance, Census, and Public Trust
AI census tools automate population analytics using satellite and mobile data. Scam detection models analyze patterns across financial and social systems to safeguard citizens. Real‑time urban data enables governance decisions that reflect demographics and demand, empowering inclusive planning.
Privacy, Ethics, and Responsible AI
AI systems depend on data aggregation, raising privacy challenges. Transparent governance frameworks, anonymization, encryption, and citizen engagement are essential for ethical adoption. Inclusive smart city deployment must address barriers such as digital divides and algorithmic bias.
Conclusion
AI truly is the backbone of modern life—powering cities, homes, businesses, healthcare, and personal devices. From predictive grids and autonomous mobility to AI‑enabled appliances and advanced bio‑innovations, the impact is vast. Strategic governance, robust privacy safeguards, and inclusive planning ensure AI enhances quality of life while preserving rights and equity. The future of urban living and human advancement lies in responsible AI integration.
FAQs
How does AI improve quality of life in smart cities?
By optimizing mobility, resource allocation, safety systems, and public services, AI enhances urban efficiency and environmental sustainability.
What are the key barriers to AI deployment in cities?
Privacy concerns, digital divides, governance transparency, and ethical use of data are primary challenges.
Can AI help predict energy demand?
Yes—AI models analyze historical and real‑time data to forecast energy usage and balance grid supply with consumption.