Introduction
The Digital immune system is an emerging framework designed to help organizations build resilient, secure, and high-performing applications in an increasingly complex digital landscape. By integrating AI-driven observability, automated testing, DevSecOps practices, and proactive cybersecurity, Digital Immune System enables early threat detection, rapid incident response, and continuous optimization across the software development lifecycle.
As businesses face growing risks from cyberattacks, system failures, and user experience issues, adopting a Digital immune system has become essential for improving reliability, reducing downtime, and ensuring scalable, future-ready digital operations.
What Is a Digital Immune System?
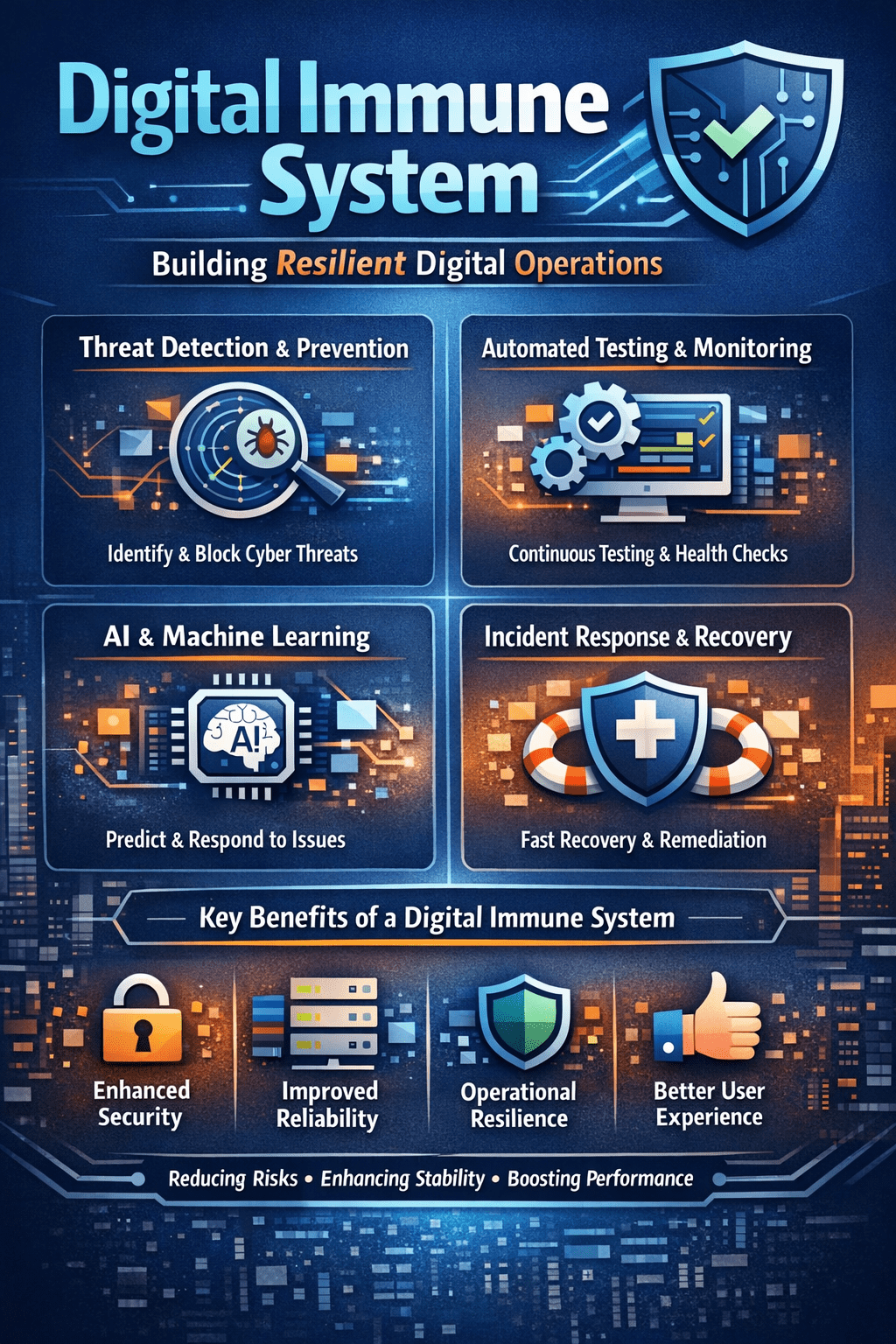
A Digital Immune System is a coordinated framework that improves application stability and security across the software lifecycle.
According to Gartner, it integrates observability, testing, security, and automated response to prevent incidents before users are affected.
Unlike traditional IT operations, which rely on manual incident handling, a Digital Immune System enables systems to sense abnormal behaviour and react automatically. IBM and ServiceNow position DIS as the next stage of intelligent IT operations for hybrid and cloud-native environments.
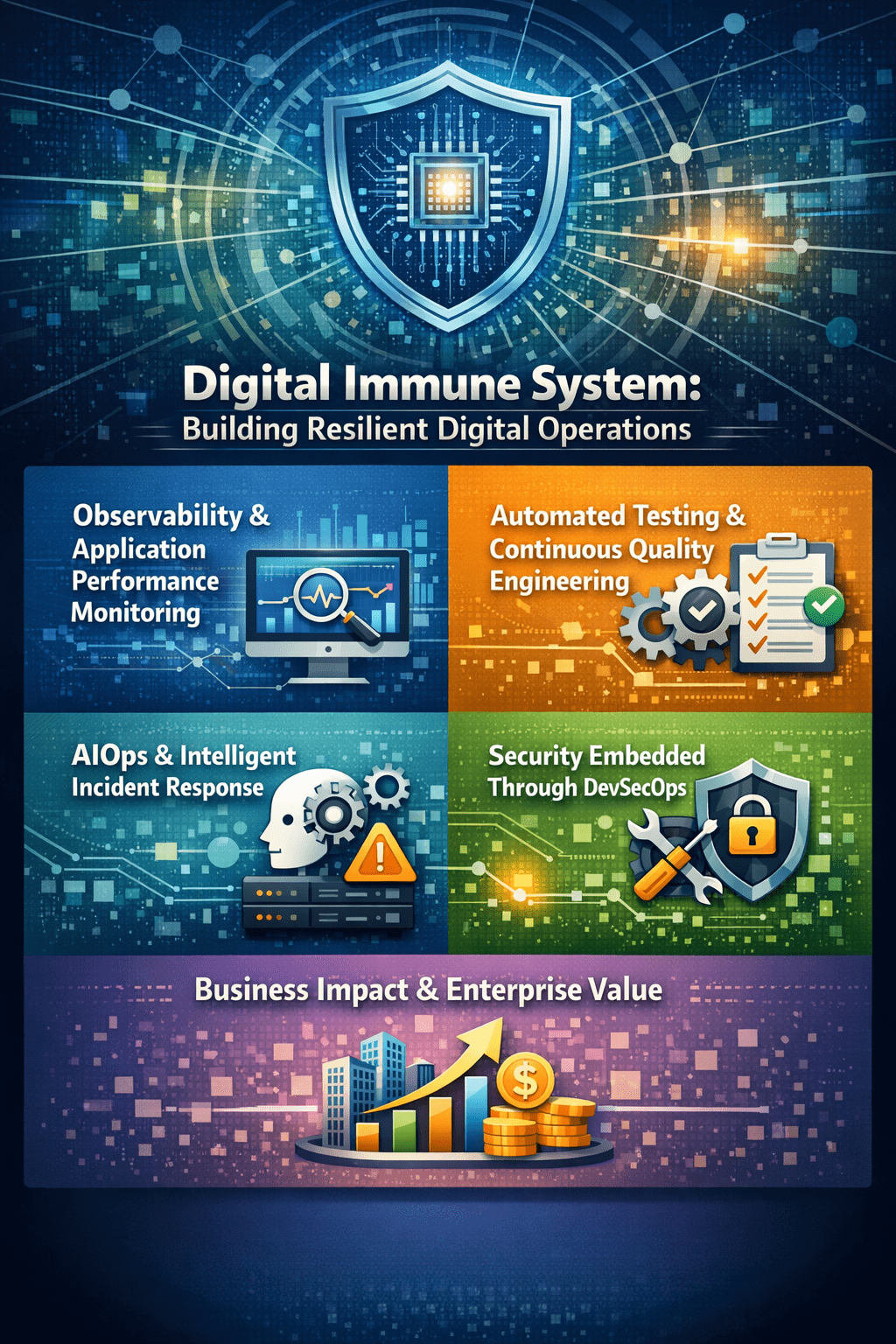
Observability and Application Performance Monitoring
Observability is the sensing layer of a Digital Immune System.
Google Cloud and AWS define observability through logs, metrics, and distributed tracing that reveal how systems behave in real time.
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) identifies latency, error rates, and service degradation early. This visibility allows teams to detect issues before they escalate, supporting faster diagnosis and system self-healing.
Automated Testing and Continuous Quality Engineering
Automated testing protects software stability as systems evolve.
Microsoft and Red Hat emphasize continuous testing as a core DevOps practice that prevents faulty code from reaching production.
Unit testing, integration testing, and regression testing validate changes across CI/CD pipelines. This reduces deployment risk and ensures reliability in fast-paced release environments.
AIOps and Intelligent Incident Response
A DIS relies on AIOps to analyze operational data at scale.
IBM and ServiceNow use machine learning to detect anomalies, correlate events, and automate incident response.
When failures occur, automated workflows can restart services, roll back deployments, or reroute traffic. This significantly reduces mean time to recovery and limits business impact.
Security Embedded Through DevSecOps
Security in a DIS operates continuously, not periodically.
Microsoft and AWS promote DevSecOps models that integrate security checks into development and runtime operations.
Runtime threat detection, zero-trust access controls, and configuration monitoring reduce exposure to cyber risk while supporting system availability.
Business Impact and Enterprise Value
A DIS delivers measurable outcomes.
Gartner and major cloud providers consistently link DIS adoption to reduced outages, improved customer experience, and lower operational costs.
By automating protection and recovery, organizations gain confidence to innovate while maintaining system stability and compliance.
Conclusion
The Digital Immune System represents a shift from reactive IT operations to self-protecting digital platforms. Supported by frameworks from Gartner, IBM, Microsoft, Google Cloud, and AWS, DIS enables systems to withstand failure and attack. Organizations that adopt a Digital Immune System position themselves for long-term digital reliability and trust.
FAQs
Who defined the Digital Immune System concept?
Gartner introduced the concept as a framework for reducing application failures.
Is a Digital Immune System a product or strategy?
It is a strategy supported by multiple tools and practices.
Why is DIS important for cloud-native systems?
Because distributed systems require automated detection and response to prevent cascading failures.