Introduction
Technology often raises fascinating questions, and one of the most common is Computer Vision. From unlocking smartphones with a glance to enabling cars to detect obstacles, this technology shapes how we interact with machines. But when we ask Computer Vision, the answer goes beyond simple definitions—it reveals how computers replicate the human ability to see and interpret the world.
Understanding Computer Vision helps us appreciate its impact on everyday life in the UK and USA, where it drives convenience, efficiency, and safety across industries. This introduction aims to make the concept approachable while highlighting its growing role in modern living.
What Is Computer Vision?
Computer vision is a branch of artificial intelligence that enables machines to analyze and interpret visual data. By converting pixels into meaningful insights, it empowers systems to detect objects, identify faces, recognize patterns, and make decisions based on imagery.
Unlike basic image processing, which focuses on improving visuals, computer vision aims to understand them. This distinction positions it as a crucial driver of automation and innovation in healthcare, transport, retail, and security.
How Does It Work?
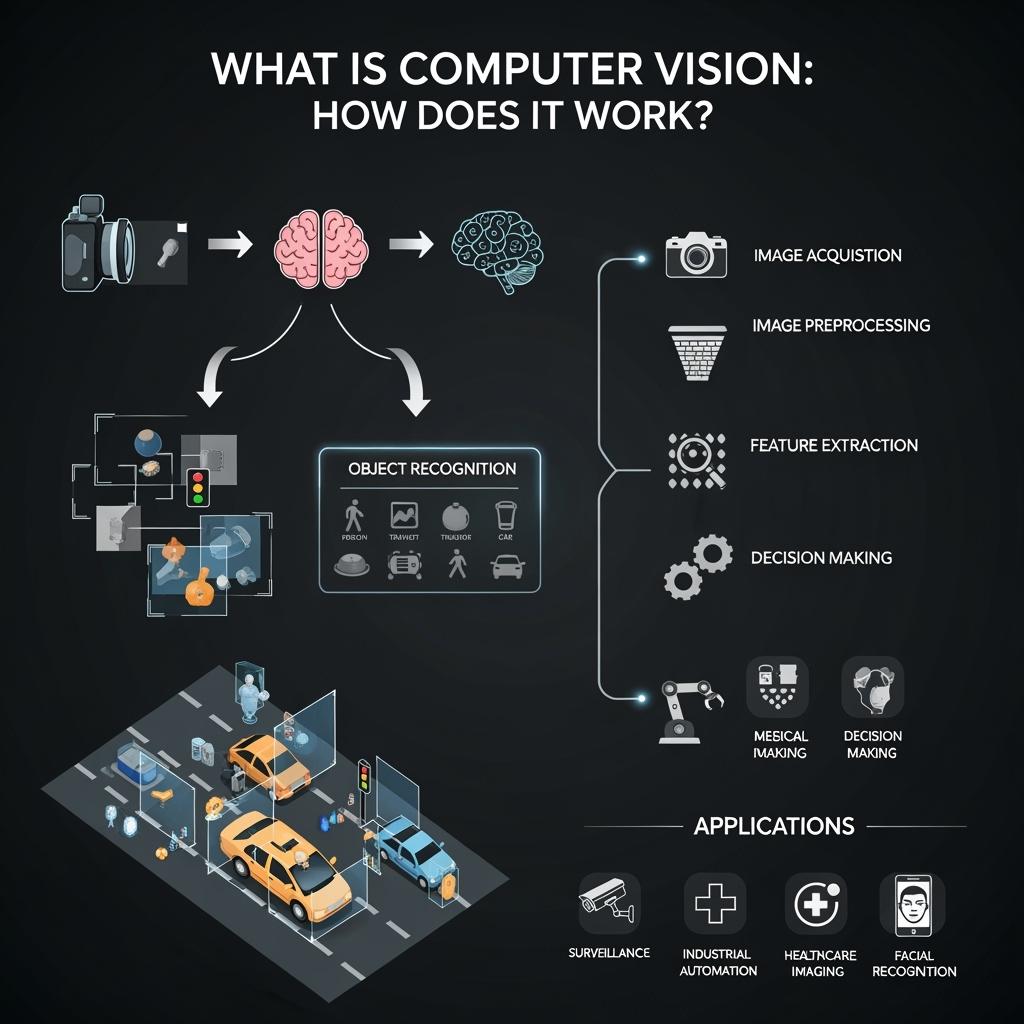
1. Image Capture
A camera, scanner, or sensor collects visual input to provide raw data.
2. Preprocessing
The system enhances image quality by reducing noise, adjusting brightness, or resizing formats.
3. Feature Extraction
Key patterns such as shapes, edges, and textures are identified to distinguish objects.
4. Recognition & Classification
AI models, often powered by deep learning, compare features against stored examples to classify or label the image.
5. Decision Making
The system outputs meaningful results, such as detecting pedestrians for self-driving cars or identifying tumors in medical scans.
Applications in the UK & USA
-
Healthcare: Hospitals use computer vision for scan interpretation, assisting clinicians in quicker and more accurate diagnoses.
-
Transport & Mobility: Autonomous driving projects in the UK and USA rely heavily on lane detection, obstacle recognition, and pedestrian safety.
-
Retail & E-commerce: Stores implement visual search and smart checkout systems to improve customer experience.
-
Security & Public Safety: Cities deploy vision-based surveillance to monitor activity and identify risks.
-
Agriculture & Infrastructure: Drones and robots analyze crops, inspect pipelines, and monitor construction sites.
With increasing adoption, industries in both nations invest heavily in vision-based solutions to reduce errors, improve efficiency, and create safer environments.
Challenges & Limitations
-
Lighting Conditions: Poor visibility or weather changes can reduce accuracy.
-
Occlusion: Hidden or overlapping objects confuse detection.
-
High Resource Demand: Real-time vision tasks require powerful hardware.
-
Bias & Fairness: Incomplete training data can cause inaccurate or unfair results.
-
Context Gaps: Machines identify objects but may miss the broader meaning humans intuitively grasp.
Why It Matters
For UK and USA users, computer vision is no longer a futuristic idea but a practical technology shaping everyday experiences. It powers security cameras, supports medical professionals, streamlines shopping, and enhances digital entertainment. By bridging the gap between sight and computation, it stands as one of the most transformative technologies of the digital era.
Conclusion
Computer vision enables machines to replicate human sight through structured steps of capture, processing, feature extraction, and classification. Its influence extends across healthcare, transport, retail, and security in the UK and USA. Despite challenges such as bias and computational demand, its value in improving efficiency and safety continues to grow.
Recommendation
If you’re interested in this field, begin with hands-on practice. Experiment with open-source libraries like OpenCV or TensorFlow for simple tasks such as image recognition. Progress to more advanced projects like object detection or medical imaging simulations. Stay connected with UK and USA tech communities to share knowledge and gain insights. Always consider ethics—focus on privacy, fairness, and transparency in your models. By approaching computer vision with curiosity and responsibility, you can position yourself at the forefront of one of today’s most exciting technologies.
FAQs
What is the main goal of computer vision?
Its goal is to help machines interpret and understand visual data in a way that supports decision-making.
How is computer vision used in daily life?
It powers facial recognition, driver-assistance systems, medical imaging, and even social media filters.
Can computer vision replace human vision?
No—it enhances specific tasks but lacks the depth, intuition, and context of human sight.