Introduction
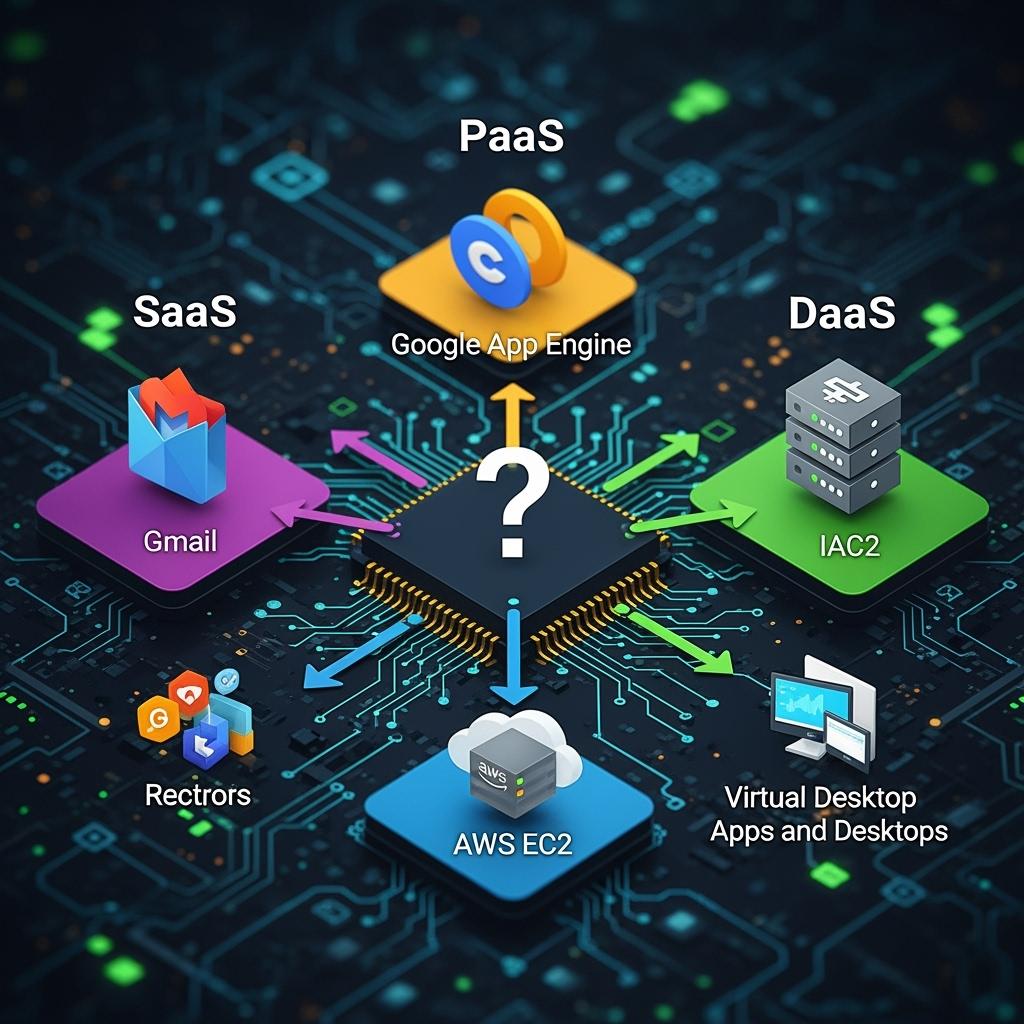
Cloud computing shapes how companies deliver software, build platforms, manage infrastructure, and support remote work. Many professionals search for “Which Applications Are SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, and DaaS?” explained with examples to understand the differences between these models. Exploring Which Applications Are SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, and DaaS? Explained with examples, it helps businesses match technology with goals, from reducing costs to scaling globally.
By learning Which Applications Are SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, and DaaS?, you gain insights into real-world tools, benefits, and strategies that drive digital transformation.
The evolution from IaaS to SaaS represents a journey from building a house from the ground up to simply renting a fully furnished apartment. The role of artificial intelligence (AI) is now accelerating this landscape, introducing new capabilities and considerations for each model. This guide provides a clear framework for classifying applications and selecting the right cloud service for your needs.
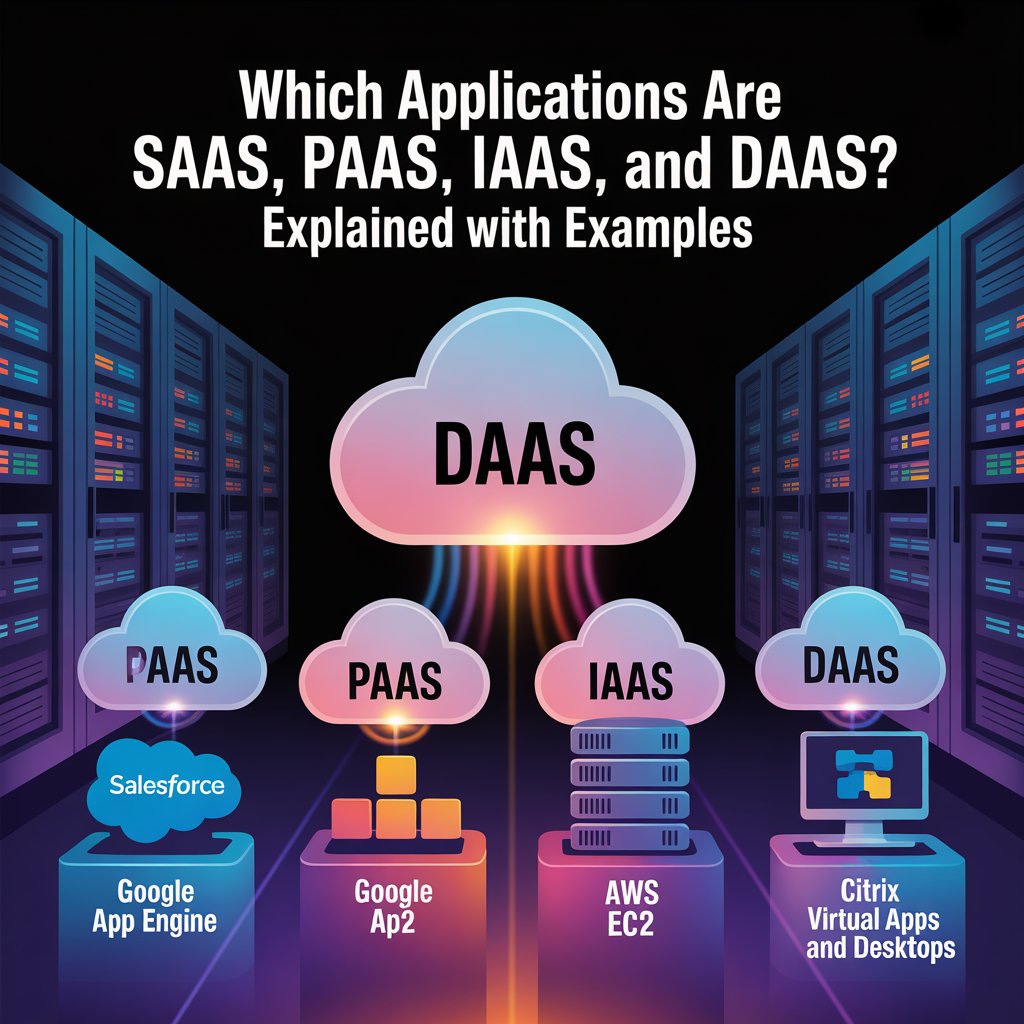
Software as a Service (SaaS): Ready-to-Use Applications
SaaS delivers complete, cloud-hosted software applications accessed over the internet, typically via a web browser. The service provider manages everything: the underlying infrastructure, middleware, application software, and all updates and security patches. Your responsibility is limited to managing user access and your own data.
Common SaaS applications include:
- Business Productivity: Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 for office suites.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Salesforce.
- Collaboration & Communication: Zoom, Slack, and Cisco WebEx.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Systems like SAP S/4HANA Cloud.
When to Choose SaaS: Opt for SaaS when you need standard, ready-to-use software with minimal IT overhead. It’s ideal for common business functions, start-ups, or short-term projects where speed, simplicity, and predictable subscription costs are priorities.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): The Developer’s Playground
PaaS provides a complete cloud-based environment—including hardware, operating systems, and development tools—for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications. Developers bring their code, and the provider manages the servers, storage, networking, and runtime environments. This model significantly accelerates development cycles.
PaaS is the foundation for:
- Application Development Platforms: Google App Engine, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Red Hat OpenShift.
- Database Management Systems: Cloud-based Azure SQL Database or Google Cloud Firestore.
- AI/ML Development Platforms: Services like Google Vertex AI or Azure Machine Learning, which provide tools for building intelligent applications without managing clusters.
When to Choose PaaS: Select PaaS when your development teams need to focus solely on coding and innovation without the burden of provisioning and managing infrastructure. It’s perfect for agile development, microservices architectures, and when leveraging advanced services like AI frameworks.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Virtualized Building Blocks
IaaS offers on-demand access to fundamental computing resources: virtualized servers, storage, and networking. It provides the highest level of control and flexibility, allowing you to run any operating system or application on rented hardware. You manage everything from the OS upward, while the provider ensures the physical data centers and hardware are available and maintained.
Typical uses for IaaS include:
- Virtual Machines and Compute: Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine.
- Scalable Cloud Storage: Google Cloud Storage or Amazon.
- Hybrid Cloud and “Lift-and-Shift” Migrations: Extending an on-premises data center to the cloud or migrating entire workloads with minimal modification.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC) & AI Training: Providing the massive, scalable compute power needed for training complex machine learning models.
When to Choose IaaS: IaaS is best when you need maximum control, have unpredictable or “spiky” workloads, or are running custom or legacy applications that require specific OS or network configurations. It demands more in-house technical expertise to configure and secure the environment.
Desktop as a Service (DaaS): The Virtual Workspace
DaaS delivers a secure, cloud-hosted virtual desktop environment to any device over the internet. It provides a consistent, managed Windows or Linux desktop experience where all applications, data, and processing occur in the cloud, not on the local device. This centralizes management and enhances security for distributed workforces.
DaaS solutions are exemplified by:
- Managed Virtual Desktop Platforms: Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops service or VMware Horizon Cloud.
- Cloud Provider Solutions: Windows 365 Cloud PC or Amazon WorkSpaces.
When to Choose DaaS: Implement DaaS to support secure remote or hybrid work, streamline IT management for a distributed workforce, or provide contractors with secure, temporary access to specific applications and data without provisioning physical hardware.
Critical Factor: The Shared Responsibility Model
A fundamental concept across all cloud models is the shared responsibility model for security and management. The division of labor shifts dramatically depending on the service you choose. A critical mistake is assuming the cloud provider is responsible for securing your data and applications in all scenarios.
- In IaaS, you are responsible for securing the operating system, applications, network configurations, and data. The provider secures the physical infrastructure.
- In PaaS, the provider’s responsibility expands to include the runtime, middleware, and OS. You focus on securing your application code and data.
- In SaaS and DaaS, the provider’s responsibility is greatest, managing the application and infrastructure. Your primary duties are user access management, data classification, and compliance.
The Role of AI Across Cloud Models
AI is not a separate service but a transformative capability integrated across SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. It adds intelligent functionality at every layer of the cloud stack.
- AI in SaaS: Adds features like predictive analytics in CRM, intelligent writing assistants in office suites, or automated insights in business intelligence tools.
- AI in PaaS: Provides developers with pre-trained machine learning models, AI APIs (for vision, language, and speech), and managed platforms (like Amazon SageMaker or Google Vertex AI) to build custom AI applications.
- AI in IaaS: Supplies the raw, high-performance compute power (GPUs/TPUs) and scalable storage necessary to train large foundational AI models from scratch.
This integration, often called AIaaS (AI as a Service), allows organizations to leverage sophisticated AI without massive upfront investment in specialized hardware and talent.
Choosing the Right Cloud Service Model for Your Business
- Match needs: SaaS suits productivity, PaaS suits developers, IaaS fits enterprise IT, and DaaS supports remote workers.
- Hybrid approaches: Many companies combine models to optimize operations.
- Decision factors: Balance cost, performance, and security to align with business goals.
Conclusion
Cloud service models like SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, and DaaS provide businesses with flexible options to meet different needs. SaaS simplifies software delivery, PaaS empowers developers, IaaS delivers scalable infrastructure, and DaaS supports remote work securely. Choosing the right model—or combining several—depends on goals, budget, and long-term strategy. With the right approach, organizations can reduce costs, innovate faster, and stay competitive in a digital-first world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main difference between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS?
SaaS delivers ready-made software, PaaS provides tools for developers, and IaaS offers virtual infrastructure resources.
Is DaaS the same as SaaS?
No, DaaS delivers virtual desktops for remote access, while SaaS delivers software applications over the internet.
Which cloud model is best for small businesses?
SaaS is often best for small businesses because it reduces IT costs and provides easy-to-use applications with minimal setup.